Ремонт и техобслуживание двигателей Deutz TCD 2013 и Deutz TCD 2012
Информация для специалистов сервиса и инженеров обслуживающих двигателя Deutz TCD 2013 и Deutz TCD 2012:
Разборка двигателя Deutz TCD 2013
Ременные передачи Deutz TCD 2013 и Deutz TCD 2012
Замена поликлинового ремня
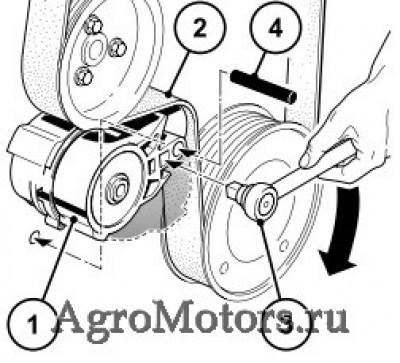
— Сначала снять поликлиновой ремень (2) с самого маленького ролика или натяжного ролика.
— Установить новый поликлиновой ремень (2).
— Удерживать натяжной ролик с помощью торцевого ключа и вынуть штифтовый ограничитель.
— Натянуть новый поликлиновой ремень с помощью натяжного ролика и торцевого ключа (3). Проверить, чтобы поликлиновой ремень правильно прилегал в своей направляющей.
Проверка удлинения ремня
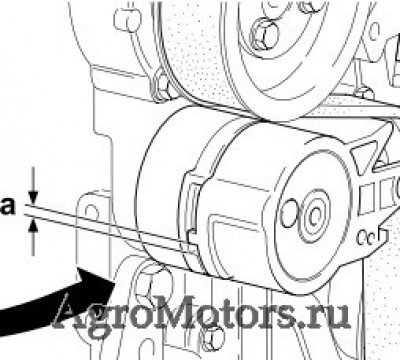
— Проверить предел износа поликлинового ремня следующим образом.
— Измерить расстояние между выступом подвижного натяжного рычага и упором неподвижного натяжного корпуса.
— Если расстояние «а» меньше 3 мм, ремень с натяжным роликом необходимо заменить.
Регулировка зазора клапанов Deutz TCD 2013 и Deutz TCD 2012
Регулировака клапанов Deutz TCD 2013 L6 4V и Deutz TCD 2013 L4 4V
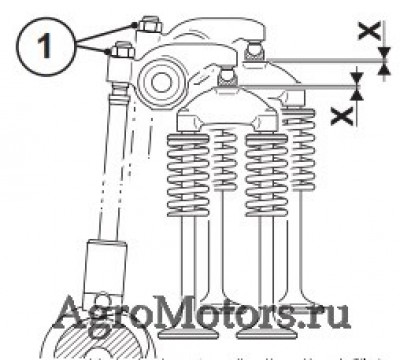
— Снять крышку головки цилиндров.
— Перед регулировкой зазора клапанов дать двигателю остыть не меньше 30 мин.: температура масла ниже 80 °C.
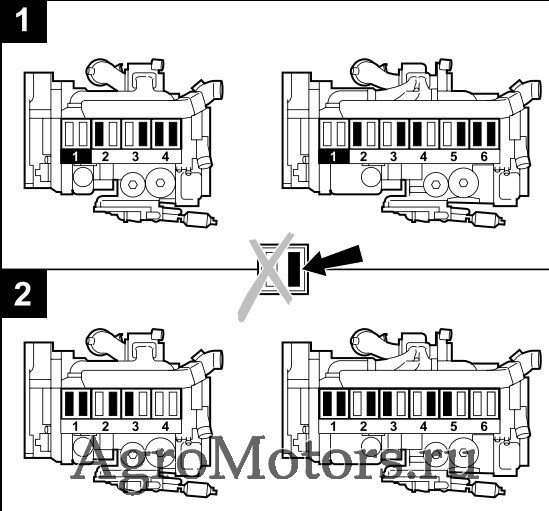
— Наложить прокручивающее устройство над крепежными болтами ременных шкивов.
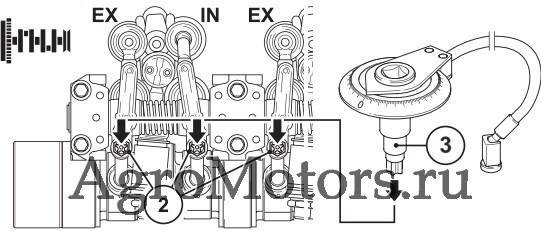
— Прокрутить двигатель, пока не будет достигнуто перекрытие клапанов, цилиндр 1. Цилиндры настраиваются согласно схеме настройки.
Указание:
— Перекрытие клапанов обозначает:
— Выпускной клапан EX еще не закрыт, впускной клапан IN начинает открываться.
— Надеть шайбу углового закручивания (3) (номер заказа: 8190) и насадку на торцевой ключ (4) (номер заказа: 8193) на винт регулировки зазора клапанов (2).
— Ослабить контргайку (1) специальным инструментом (номер заказа: 8199).
— Зафиксировать магнит шайбы углового закручивания.
— Поворачивать шайбу углового закручивания по часовой стрелке до прилегания (коромысло клапана без зазора) и установить шкалу на ноль.
— Поворачивать шайбу углового закручивания против часовой стрелки, пока не будет достигнут заданный градус угла закручивания:
— Зафиксировать шайбу углового закручивания (3) от перекручивания.
— Затянуть контргайку (1) (момент затяжки 20 Нм).
— Выполнить регулировку на каждом цилиндре.
— Установить уплотнение (при необходимости новое).
— Визуально проверить и при необходимости заменить винты и резиновые элементы.
— Установить крышку головки цилиндров (при необходимости с новым уплотнением) и затянуть винты согласно инструкции: 9 Нм
— Повернуть воздушный клапан в положение и закрепить.
Схема настройки зазора клапанов
— Соответствие фаз распределения на коленчатом и распределительном вале при новом монтаже обеспечивается отметками на шестернях.
— Коленчатый вал может поворачиваться различными прокручивающими устройствами.
Положение коленчатого вала 1
— Поворачивать коленчатый вал, пока оба клапана на цилиндре 1 не перекроются (выпускной клапан еще не закрыт, впускной клапан начинает открываться.)
— Настраиваемые коромысла клапанов в начальном состоянии / при поставке имеют зазор.
Настройка зазора клапанов:
— Ослабить контргайку на обозначенных коромыслах клапанов (см. рисунок).
— Регулировочный винт по угловому методу IN = 75° EX = 105°
— Затянуть контргайку с моментом затяжки 20 Нм.
Положение коленчатого вала 2
— Повернуть коленчатый вал на один оборот, то есть 360°, перекрытие клапанов на цилиндре 4 или 6 в зависимости от модели.
— Теперь установить обозначенные на рисунке 2 коромысла клапанов, как описано выше.
Регулировака клапанов Deutz TCD 2012 L6 4V и Deutz TCD 2012 L4 4V
— Наложить прокручивающее устройство над крепежными болтами ременных шкивов.
— Перед регулировкой зазора клапанов дать двигателю остыть не меньше 30 мин.: температура масла ниже 80 °C.
— Инструмент ( 86).
— Прокрутить двигатель, пока не будет достигнуто перекрытие клапанов, цилиндр 1. Цилиндры настраиваются согласно схеме настройки.
Указание:
— Перекрытие клапанов обозначает:
— Выпускной клапан EX еще не закрыт, впускной клапан IN начинает открываться.
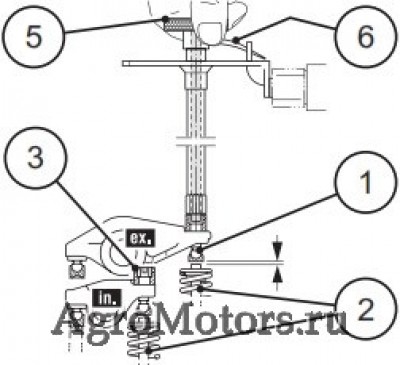
— Для этого ослабить все контргайки (3) настраиваемого коромысла.
— Повернуть регулировочные винты (1) против часовой стрелки на один оборот назад.
— Закрутить регулировочный винт (1) на настраиваемом коромысле в направлении часовой стрелки без зазора. То есть, между коромыслом клапана и клапаном (2) не должно быть зазора, а на клапан не должно оказываться давление.
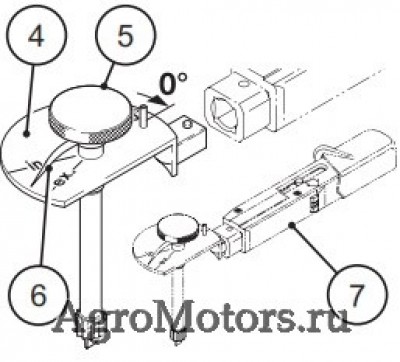
— Установить стрелку (6) на рифленой ручке (5) измерительной пластины (4) на „0°“, при этом больше не перекручивать рифленую ручку (5).
— Удерживать измерительную пластину (4) точно в этом положении и поворачивать регулировочный винт (1) ручкой (5) против часовой стрелки, пока стрелка (6) не будет стоять на отметке „in“ или „ex“.
— Удерживать ручку (5) точно в этом положении и закрутить контргайку (3) динамометрическим ключом (7) с моментом затяжки 20 Нм.
— Выполнить регулировку на каждом цилиндре.
— Установить уплотнение (при необходимости новое).
— Визуально проверить и при необходимости заменить винты и резиновые элементы.
— Установить крышку головки цилиндров (при необходимости с новым уплотнением) и затянуть винты согласно инструкции: 9 Нм.
— Повернуть воздушный клапан в положение и закрепить.
Регулировка зазора клапанов для двигателя TCD 2013 L4 4V
| Последовательность зажигания: 1 — 3 — 4 — 2 | ||||
| Клапаны | Цилиндр | |||
| перекрытие | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| регулировка | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Перекрытие клапанов | ||||
| Выпускной клапан еще не закрыт, впускной клапан начинает открываться | ||||
Регулировка зазора клапанов для двигателя TCD 2013 L6 4V
| Последовательность зажигания: 1 — 5 — 3 — 6 — 2 — 4 | ||||||
| Клапаны | Цилиндр | |||||
| перекрытие | 1 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 4 |
| регулировка | 6 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
| Перекрытие клапанов | ||||||
| Выпускной клапан еще не закрыт, впускной клапан начинает открываться | ||||||
Регулировка моторного тормоза Deutz TCD 2013 и Deutz TCD 2012
Проверка и настройка зазора управляющего золотника в моторном тормозе
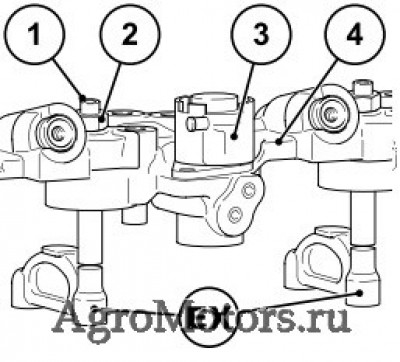
2 Контргайка
3 Электромагнитный клапан (электронное управление)
4 Управляющий мостик
— После настройки зазора клапана.
– Блок управления для моторного тормоза уже установлен.
— Прокрутить двигатель, пока не будет достигнуто перекрытие клапанов, цилиндр 1.
— Выполнить зазор управляющего золотника на каждом выпускном клапане.
— Затем выполнить те же действия, что и при зазоре клапанов.
Указание:
Перекрытие клапанов обозначает: Выпускной клапан еще не закрыт, впускной клапан начинает открываться, см. схему настройки клапанов.
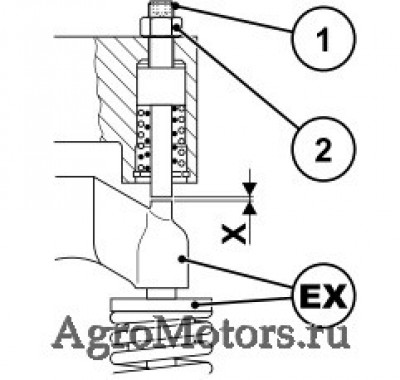
— Открутить контргайку (2).
— Надеть зазор управляющего золотника X с регулировочным устройством ( 64) на регулировочный винт (1) в EX и настроить следующим образом:
– Зафиксировать магнит
– Затем повернуть под угловым градусом 432° назад (рукой или динамометрическим ключом):
– Поворачивать регулировочное устройство без зазора, пока управляющий золотник не будет прилегать к клапанному мостику, при этом установить шкалу на «0».
EX = выпускной клапан 432° при резьбе M8 (соответствует зазору 1,5 мм)
— Выполнить проверку или регулировку на каждом цилиндре.
— Снова установить крышку головки цилиндров с новым уплотнением.
— Повернуть воздушный клапан в положение и закрепить.
EX = выпускной клапан
Источник
Deutz PDF Service Manuals, Fault Codes and Wiring Diagrams
Deutz 2008-2009 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz 226B Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz D 2008-2009 Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine D2008 2009 Workshop Manual PDF.pdf
Deutz Engine Fire Protection — Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine S-BV6-8-9M628 Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz FL 411 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz FL 413 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz Serie 7 Agrotron Service Manual.pdf
Gt-50dz Tow Tractor With Deutz Engine.pdf
Deutz 1011 Parts Manual.pdf
Deutz 2008-2009 Parts Manual.pdf
Deutz 413 Parts Manual.pdf
Deutz 912 Parts Manual.pdf
Deutz 914 Parts Manual.pdf
Deutz Accessories Catalogue.pdf
Deutz BF4M1013C Spare Parts Catalogue.pdf
Deutz 912-913 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz 912-913 Workshop Manual Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz 912-913 Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz 914 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine 914 Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 1.pdf
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 2.pdf
Deutz Engines B_FM 1008_F Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz 0312 1936 2011 Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz 1011F Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz BF4m1011F Engine Service Parts Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine 1011F Werkstatthandbuch.pdf
Deutz Engine 1011F Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Engine Description.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Engine Operation.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Engine Preservation.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Faults, Causes and Remedies.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — General.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Notes.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Operating Media.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Routine Maintenance.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Service and Maintenance.pdf
Deutz Engine B-F L 1011F B-FM 1011F Operation Manual — Technical Specifications.pdf
Deutz Engine B-FL 1011F Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz F3M 1011F, BF3M, F4M, BF4M Service Manual.pdf
Deutz 1012 1013 Operation and Maintenance Manual.pdf
Deutz 1012-1013 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine 1012-1013 Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz 1015 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz BFM 1015 Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz 0312 1936 2011 Workshop Manual- competence level 3.pdf
Deutz 0312 4004 2011 Workshop Manual- competence level 2.pdf
Deutz 2011 — Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz D 2011 w, TD 2011 w, TCD 2011 w Workshop Manual- competence level 2.pdf
Deutz D 2011, TD 2011 Workshop Manual- competence level 2.pdf
Deutz Engine B-FL-FM 2011 Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz 2012 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine 2012 Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine BF6M 1013 Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine BFM-2012 Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz TCD 2012-2013 Service Manual.pdf
Deutz TCD2012 Instruction Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 2V Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Care and maintenance work.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Engine corrosion protection.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Engine description.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Faults, causes and remedies.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — General.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Maintenance.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Operating substances.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Operation Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Operation.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Service.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2013 L04-06 4V Instruction Manual — Technical data.pdf
Deutz TCD 2013 4V — Industry Workshop Manual.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2015 Workshop Manual — General.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2015 Workshop Manual — Job card overview.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2015 Workshop Manual — Special tools.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2015 Workshop Manual — Standart tools.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2015 Workshop Manual — Technical data.pdf
Deutz Engine TCD 2015 Workshop Manual — User notes.pdf
Deutz TCD 2015 Service Manual.pdf
Parts manuals
The German company Deutz AG has been producing engines for more than 130 years. Its emblem on diesel engines and gas engines is evidence of the highest quality of products, in which the rich experience of several generations of talented German engineers and technicians is accumulated. The range of power units offered in 2001 includes dozens of basic models of motors for various purposes with a power from 4 to 7,400 kW. The long way of Deutz AG to today’s achievements begins in the distant 1864. We will get acquainted with its main stages, especially since in the history of the firm there were mutually beneficial contacts with our country.
So, the year 1864-th. German designer and inventor Nikolaus Otto, one of the first creators of an efficient internal combustion engine, gets acquainted with an entrepreneur from Cologne, Evgeny Longen, a very wealthy and technically competent man, and inspires him to create a company that would manufacture industrial combustion engines-atmospheric gas engines.
Longen helps Otto to obtain a patent for the engine and conducts a «wide advertising campaign», demonstrating the motor at many exhibitions in the Old and New World. Finally, in 1867, the sample was awarded a gold medal at an exhibition in Paris, and interest in it reached the level at which it was worth starting its production. In 1869, launched a large plant near Cologne, in the suburbs of Doitz. The new enterprise is named after the names of its owners «Longen, Otto and Roosen». At the same time, the license for the production of the internal combustion gas engine of the English company Crossley is being sold.
So, in the Old World a new compact energy source appeared on the market, ready to compete with bulky steam engines. In 1872 a new technical director — Gottlieb Daimler (the future inventor of the car) was appointed to the reconstructed enterprise, and Wilhelm Maybach — the person no less legendary in the automotive industry — became the head of the design department. The company receives the new name Gasmotoren-Fabrik Deutz AG and expands the scope of application of engines.
In 1879 Nikolaus Otto successfully completes the experiment to create the world’s first four-stroke engine with compression of the fuel-air mixture before its ignition — the prototype of most modern gasoline engines. Encouraged by the success, the enterprise is again being reconstructed and preparing for a new round of development, despite the departure of G. Daimler and V. Maybach from it. In 1886, Otto received his Ph.D. from the University of Wurzburg and, together with Robert Bosch, developed an electrical ignition system.
So, working engines that consumed a gasoline mixture, appeared. They are compact, fast and affordable. And all this, thanks to the pioneer of engine building, the company Deutz. In 1896, the history of the automobile industry begins. At the same time much more powerful gasoline engines began to be installed on railroad locomotives.
However, the technical department of the company was not asleep. In 1898, a fundamentally new engine was constructed and presented to the public, having compression ignition. In honor of the author, Rudolf Diesel, he was called a diesel engine. A new era in motor-building began.
By 1907, the design of the first sample had been worked out and patented; It was possible to start the production of diesel engines. Their consumption increased, and the size range expanded. After the short-term production of Deutz-Bugatti cars (1907 — 1912) with the participation of the very creator, Ettore Bugatti, who worked in the company from 1907 to 1909, the management turned its eyes to the tractors. The first machine of its own design came off the assembly line in 1924. The model was called Deutz MTN 222 and was equipped with special pulleys for driving agricultural equipment.
At the same time, different types of engines were produced — for cars and trucks, rail cars, as well as industrial engines that were sent to other companies. Since 1921 the company was officially called Motorenfabrik Deutz AG. In 1938 — the next transformation. Having acquired new plants, the company became known as Klockner-Humboldt-Deutz AG (KHD). In the same year, its technical department developed another novelty — the first diesel with air cooling. However, soon everything changed abruptly. The bombing of factories by aircraft of the USSR and its allies destroys 74% of the entire industrial potential of the concern. It was, as can be easily guessed, in late 1944 — the first half of 1945.
A new stage, called «restoration of former grandeur,» began in 1949. It was then that management decided to resurrect the production of agricultural tractors with air-cooled diesel engines. The goods were dispersed in the market instantly. Gradually, together with the tractors, the production of trucks and buses began, which bore the brand of Magirus-Deutz and was considered one of the best in Europe.
By 1964, a new Technical Center was built near Cologne, which increased the competitiveness of the structures being built. Machines with the KHD brand (dump trucks, construction chassis, diesel engines) have been exhibited many times since 1964 at exhibitions in Moscow and have been evaluated by domestic experts. When the construction of the Baikal-Amur Mainline began, Deutz AG received an unprecedented order for the supply in the USSR of 10,000 (!) First-class dump trucks that formed the basis of the contractors’ car fleet. Striking, but true: some of them are still on the go.
After the purchase of the USSR, the license for the right to produce Deutz diesel engines with air cooling, the specialists of the German company together with Russian engineers did a great job of conducting full-scale tests of the motors on trucks Ural-375D, the ones for which they were intended. The design of the diesel engines was fully adapted to operation at temperatures from -40 to + 40 ° C. The work was carried out in 1966 — 1980 gg. As a result, a plant was built in Kustanai (now the Republic of Kazakhstan), designed to supply several tens of thousands of motors per year. It was not possible to launch this enterprise before 1991, and then the Soviet Union did not. However, the experience gained in researching diesel engines under extreme conditions has benefited both Deutz specialists and ours.
In 1975, the brand Magirus-Deutz disappeared from the automobile directories of current products. The truck and bus division was part of IVECO, a multinational concern controlled by FIAT. And the company Deutz AG continued to engage in engine construction and tractors. In 1978, the production of a 4 millionth internal combustion engine was commemorated in the year 1867. The next such event occurred only in 1989. And also in connection with the release of a 4 millionth diesel engine, but only with air cooling. Their production began in 1944. In 1995, the department for the production of tractors and agricultural machines was sold to the Italian company Same Group, and the firm Deutz AG focused on where it started: the engines supplied to a wide variety of manufacturers. «Everything has returned to normal.»
However, the history of this amazing company does not end there . There are still many interesting projects ahead of it, among them . the organization of the assembly of Deutz diesel engines in Russia. Were you surprised? Nothing surprising. We need good diesel engines, and Russia needs Deutz AG. That’s all.
Источник